constant tension hose clamp supplier
Compliant with the SAE J1508 standard,Type”SLHD”/Type “SLF”
Constant tension hose clamp is worm gear driven hose clamps, widely used in heavy-duty trucks, high-performance cars, ships, and heavy-duty industrial fields. They feature high torsional strength, good pressure resistance, balanced torsional torque, and a compensating washer to effectively compensate for temperature changes, adapt to increases or decreases in joint diameter, prevent clamp loosening and load loss due to temperature changes, ensure no leakage, and are corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and high-strength.
This type of clamp belongs to the clamps for worm driven clamps,which adopts a disc spring stucture. SLHD series-Heavy Duty Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp 5/8″ wide band.SLF series-Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp 9/16″ wide band.
Basic structure of constant torque clamp
screw
Extend hexagon screw,multiple materials,and head sizes are available for selection
disc spring
provide continuus toque compensation
upper cover/base
a robust split-housing design
band/protectire liner
prevents damage to be hose or tube
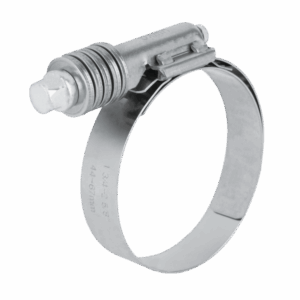
HWKG models of constant tension hose clamp
ZG14Q
Band/
Protectire Liner
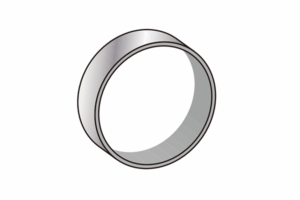
Stainless Steel
Upper Cover/Base
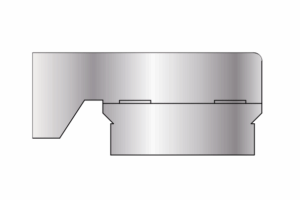
Stainless Steel
Disc Spring

Stainless Steel
Hex Head
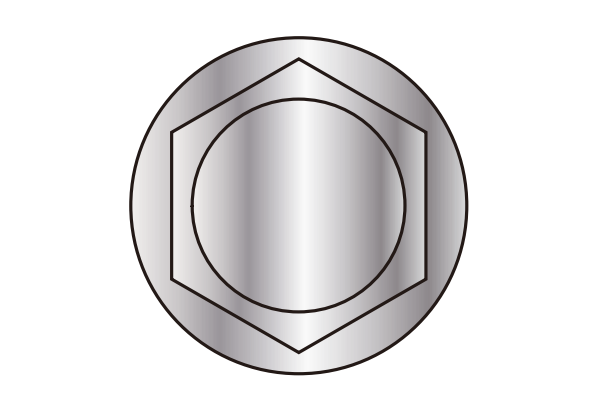
Stainless Steel
ZG14B
Band/
Protectire Liner

Stainless Steel
Upper Cover/Base

Stainless Steel
Disc Spring

Stainless Steel
Hex Head

carbon steel or 400 series Stainless Steel
ZG16Q
Band/
Protectire Liner

Stainless Steel
Upper Cover/Base

Stainless Steel
Disc Spring

Stainless Steel
Hex Head

Stainless Steel
ZG16B
Band/
Protectire Liner

Stainless Steel
Upper Cover/Base

Stainless Steel
Disc Spring

Stainless Steel
Hex Head

carbon steel or 400 series Stainless Steel
constant pressure hole clamp configuration table
| SPECIFICATION | MATERIAL | Band/Protective Liner | Upper Cover/Base | Disc Spring | SCREW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZG14B ZG16B |
W2 | 200/300 series stainless steel | 200/300 series stainless steel | 400 series stainless steel | carbon steel |
| W3 | 200/400 series stainless steel | 200/300 series stainless steel | 300/400 series stainless steel | 400 series stainless steel | |
| ZG14Q ZG16Q |
W4 | 200/300 series stainless steel | 200/300 series stainless steel | 300/400 series stainless steel | 300 series stainless steel |
| W5 | 316 stainless steel | 316 stainless steel | 316 stainless steel | 316 stainless steel | |
| Customization of specifications and material configurations is available based on customer requirements. The above information is for reference only and should not be considered as technical specifications | |||||
constant torque clamp specification table
| RANGE | SPECIFICATION | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RANGE mm | RANGE IN | ZG14Q | ZG14B |
| 14-27 | 9/16″-1 1/16″ | ● | ● |
| 17-32 | 11/16″-1 1/4″ | ● | ● |
| 19-38 | 3/4″-1 1/2″ | ● | ● |
| 21-44 | 13/16″-1 3/4″ | ● | ● |
| 27-51 | 1 1/16″-2″ | ● | ● |
| 33-57 | 1 5/16″-2 1/4″ | ● | ● |
| 40-64 | 1 9/16″-2 1/2″ | ● | ● |
| 46-70 | 1 13/16″-2 3/4″ | ● | ● |
| 52-76 | 2 1/16″-3″ | ● | ● |
| 59-83 | 2 5/16″-3 1/4″ | ● | ● |
| 65-89 | 2 9/16″-3 1/2″ | ● | ● |
| 71-95 | 2 13/16″-3 3/4″ | ● | ● |
| 78-102 | 3 1/16″-4″ | ● | ● |
| 84-108 | 3 5/16″-4 1/4″ | ● | ● |
| 90-114 | 3 9/16″-4 1/2″ | ● | ● |
| 103-127 | 4 1/16″-5″ | ● | ● |
| 121-143 | 4 25/32″-5 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 130-152 | 5 1/8″-6″ | ● | ● |
| 141-165 | 5 9/16″-6 1/2″ | ● | ● |
| 152-178 | 6″-7″ | ● | ● |
| SAE Size No. | RANGE | SPECIFICATION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RANGE mm | RANGE IN | ZG16Q | ZG16B | |
| – | 25-45 | 1″-1 3/4″ | ● | ● |
| – | 27-51 | 1 1/16″-2″ | ● | ● |
| 212 | 32-54 | 1 1/4″-2 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| 262 | 44-67 | 1 3/4″-2 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 312 | 57-79 | 2 1/4″-3 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| 362 | 70-92 | 2 3/4″-3 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 412 | 83-105 | 3 1/4″-4 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| – | 90-114 | 3 9/16″-4 1/2″ | ● | ● |
| 462 | 95-117 | 3 3/4″-4 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 512 | 108-130 | 4 1/4″-5 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| 562 | 121-143 | 4 3/4″-5 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 612 | 133-156 | 5 1/4″-6 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| 662 | 146-168 | 5 3/4″-6 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 712 | 159-181 | 6 1/4″-7 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| 762 | 171-194 | 6 3/4″-7 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 812 | 184-206 | 7 1/4″-8 1/8″ | ● | ● |
| 862 | 197-219 | 7 3/4″-8 5/8″ | ● | ● |
| 912 | 210-232 | 8 1/4″-9 1/8″ | ● | ● |
HWKG 'S Production Management
Reliance on Advanced Quality Systems and Skilled Personnel
HWKG operates under a robust quality management framework aligned with automotive-grade standards such as IATF16949. Skilled engineers and trained technicians oversee every stage of the production cycle, ensuring precision and repeatability. With strict incoming, in-process, and final inspections, the team maintains consistent product integrity and delivers reliable performance for demanding applications.


Strategic Automation for Efficiency and Consistency
To enhance stability and reduce human-dependent variations, HWKG integrates self-developed automated assembly lines across key processes. Automated feeding, forming, and torque-control systems help maintain uniform quality while increasing throughput. This strategic use of automation not only boosts efficiency but also ensures every clamp meets stringent dimensional and functional requirements.
Comprehensive Certifications and Full-Service Solutions
HWKG supports its production strength with comprehensive certifications and complete testing capabilities, including torque, corrosion, durability, and material verification. Beyond manufacturing, the company provides full-service support—from customized development and rapid prototyping to flexible OEM/ODM cooperation—offering customers a reliable, end-to-end solution for diverse fastening needs.







Applications of Constant tension hose clamp
Industrial and Heavy-Duty Systems
A constant tension hose clamp performs reliably in industrial and heavy-duty systems where equipment experiences load shifts, thermal cycling, or extended run time. Its self-adjusting design maintains stable sealing, making it suitable for manufacturing machinery, pumps, compressors, and other applications that demand long-term, maintenance-reduced performance.
Engine & Exhaust with Automotive Constant Tension Hose Clamps
In exhaust, cooling, and engine assemblies, automotive constant tension hose clamps maintain sealing despite heat expansion, vibration, and aging. Compared with standard clamps, a Constant Torque Hose Clamp continually adjusts tension, helping prevent leaks and ensuring stable connections in critical automotive thermal-management and air-handling systems.
Pressure- or Temperature-Fluctuating Applications
Systems that undergo repeated pressure or temperature shifts benefit from a constant tension clamp that compensates for hose deformation. Whether used as a constant pressure hose clamp or torque-controlled design, it delivers consistent sealing performance in boilers, fluid-transfer lines, HVAC units, and other fluctuation-prone environments.
High-Vibration Environments
A constant tension worm gear clamp maintains stability in high-vibration conditions where ordinary clamps loosen over time. Its self-adjusting mechanism absorbs movement and preserves compression, making it ideal for off-road equipment, generators, marine engines, and other applications exposed to continuous motion.
Key Features of Constant Torque Worm Clamps
Built with reinforced materials and precision components, the Constant Torque Hose Clamp ensures durability in demanding environments. Its heavy-duty construction provides excellent resistance to vibration, load changes, and thermal shifts, making it a trusted option among constant tension worm gear clamp designs.
The disc spring washer stack provides the core stability of a Constant Torque Worm Drive Clamp, allowing it to maintain steady tension even under temperature cycling. This structure ensures the constant tension hose clamp delivers consistent torque compensation, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable long-term sealing performance.
A responsive spring mechanism enables the constant tension clamp to adjust automatically as hoses expand or contract. This feature helps the Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp maintain uniform pressure and prevents leakage, offering a dependable solution where a constant pressure hose clamp is required.
The liner-integrated structure protects the hose surface while enhancing sealing efficiency. This design helps the Constant Tension Worm Driven Clamp maintain even pressure distribution, reducing wear and ensuring consistent performance. It is especially suitable for applications needing a secure constant tension worm drive hose clamp that prevents cold-flow or extrusion.
The tooth guard part is equipped with a positioning groove accessory to prevent the tooth guard pad from tilting to one side during the locking process, which can effectively protect the hose from being cut by the tooth holes.
What Materials and Technologies Are Used in Constant Tension Hose Clamps?
Engineered Polymers for Enhanced Performance
Engineered polymers are used to reduce friction, improve sealing surfaces, and enhance vibration resistance. When integrated into a Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp or a Constant Torque Clamp, these materials help maintain uniform pressure distribution and boost long-term stability, especially in dynamic or temperature-variable environments.
Precision Manufacturing
Precision-controlled manufacturing ensures every Constant Tension Worm Driven Clamp meets strict dimensional and functional standards. With accurate forming, torque calibration, and quality inspection, each constant tension hose clamp delivers consistent performance, supporting reliable sealing across a wide range of applications.
Stainless Steel Construction
High-grade stainless steel is the foundation of a durable constant tension hose clamp. Its corrosion resistance and strength ensure long-lasting performance. Whether used in a Constant Torque Hose Clamp or a constant tension worm gear clamp, stainless steel construction helps maintain reliable tension and consistent sealing.
Special Spring Mechanisms
Advanced spring mechanisms enable a constant tension clamp to automatically adjust to hose expansion and contraction. These systems ensure stable pressure, making the design suitable for both constant pressure hose clamp applications and Constant Torque Worm Drive Clamps that require dependable torque compensation during thermal cycling.
How Do Constant Tension Hose Clamps Differ from Regular Hose Clamps?
Automatic Adjustment and Temperature Compensation
A constant tension hose clamp automatically adjusts to hose expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes. Unlike regular clamps that require manual retightening, a Constant Torque Clamp maintains stable pressure, ensuring reliable performance and reducing the risk of leaks in fluctuating operating conditions.
Consistent Sealing and Uniform Compression
With its spring-loaded design, a constant tension clamp provides uniform compression across the hose surface. This helps a constant pressure hose clamp maintain consistent sealing even as materials shift over time, offering more dependable performance than standard clamps that may gradually lose tension.
Vibration Resistance and Anti-Loosening Stability
A constant tension worm gear clamp offers better resistance to vibration and shock, keeping the connection secure in dynamic environments. Compared to regular clamps that may loosen under movement, a Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp maintains steady force, preventing leaks and improving long-term system stability.
Heavy-Duty Durability and Long-Term Performance
Built for demanding applications, a Constant Torque Hose Clamp provides enhanced durability and long service life. Its reinforced structure and controlled tension help withstand pressure changes, vibration, and thermal cycling, outperforming regular clamps that are more prone to fatigue and performance decline over time.
How HWKG's Constant Pressure Hose Clamps Counteract Cold Flow


By Using Spring Hose Clamps
A constant tension hose clamp uses a spring-based mechanism that continuously applies adaptive pressure to the hose. This design allows the clamp to respond to changes in hose thickness caused by cold flow. Unlike rigid designs, a spring-loaded constant tension clamp maintains reliable compression, preventing gaps or leaks as materials soften or settle over time. This makes it more effective than standard clamps in long-term sealing applications.
Consistent sealing through movement
A Constant Torque Hose Clamp maintains sealing integrity by allowing controlled movement within its spring system. As the hose material shifts due to cold flow or temperature fluctuations, the clamp adjusts automatically to preserve uniform compression. This capability helps a constant pressure hose clamp avoid tension loss, ensuring the sealing interface stays tight. With continuous micro-adjustments, the clamp minimizes leakage risks in both dynamic and static operating environments.
Compensating for Material Deformation Over Time
Cold flow causes hose materials to deform gradually, reducing thickness and compromising sealing. A constant tension worm gear clamp compensates for this by applying steady, self-adjusting force as the hose settles. The mechanism automatically increases compression when deformation occurs, ensuring long-term sealing stability. Compared with traditional clamps that loosen as materials change, a Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp maintains dependable performance and prevents pressure loss in extended use.
Common Mistakes When Using constant tension worm gear clamp
Many issues with constant tension worm gear clamps come from improper installation. Common mistakes include applying too much or too little torque, or choosing a clamp type that doesn’t match the hose, size, or operating conditions. Correct selection and proper tensioning are key to ensuring reliable sealing performance.
Over-tightening a constant pressure hose clamp
Over-tightening a constant tension hose gear clamp reduces its ability to self-adjust as the hose expands or contracts. Excessive force can damage the sealing surface and can prevent the Constant Pressure Hose Clamp from maintaining proper tension, eventually leading to leaks and premature hose wear.
Under-tightening a constant torque hose clamp
Under-tightening a constant tension clamp limits the spring’s ability to apply consistent pressure. Without enough initial preload, even a well-designed Constant Torque Hose Clamp may fail to compensate for temperature changes or cold flow, resulting in inadequate sealing performance over time.
Incorrect constent tension clamp Selection for Installing
Choosing the wrong type or size of clamp reduces overall effectiveness. A constant tension clamp must match the hose diameter, material, and operating conditions. Using a standard clamp where a Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp is required can lead to instability, leaks, and frequent retightening.
How to tighten a constant tension worm clamp?
Preparing the Hose and Fitting
Before installing a constant tension hose clamp, ensure the hose and fitting are clean, undamaged, and fully seated. Proper preparation allows the Constant Torque Clamp to apply even pressure and prevents early leaks caused by debris, misalignment, or surface irregularities.
Positioning the Clamp
Place the constant tension clamp behind the hose bead or at the recommended sealing zone to ensure uniform compression. Correct positioning helps a Constant Tension Worm Drive Clamp maintain stable tension as the hose expands or contracts during operation.
Tighten to Specified Torque
Use manufacturer’s specified torque when tightening a Constant Torque Hose Clamp. Applying a correct preload allows the spring mechanism to function properly, enabling a clamp to maintain consistent pressure and prevent overtightening or loss of adjustment capability.
Recheck Tension Under Temp & Pressure
After installation, recheck the constant pressure hose clamp once the system experiences temperature or pressure changes. As materials settle or cold flow occurs, confirming tension ensures the constant pressure hose clamp continues delivering reliable sealing over time.
constant tension worm gear clamp FAQ Guide
01 Can constant tension clamps be reused?
Yes, constant tension clamps can usually be reused, but their reusability depends heavily on their condition after previous service cycles. These clamps are built with spring mechanisms that maintain consistent pressure, allowing them to endure repeated thermal expansion and contraction without losing performance. However, before reinstalling a used clamp, it’s important to inspect the band, housing, and spring elements for signs of fatigue, corrosion, warping, or reduced elasticity. Any deformation or weakened spring force can compromise the clamp’s ability to maintain sealing pressure over time. In critical applications—such as automotive cooling systems or industrial fluid lines—manufacturers may recommend replacing the clamp instead of reusing it to ensure maximum reliability and prevent unexpected leaks.
02 How does a constant tension hose clamp work?
A constant tension hose clamp works by using an integrated spring element—such as a disc spring or wave spring—to automatically adjust its clamping force.
As temperature changes cause the hose and fitting to expand or contract, the spring compensates for these dimensional shifts.
When the hose shrinks, the spring adds pressure to maintain sealing force.
When the hose expands, the spring compresses slightly to prevent damage or over-tightening.
This self-adjusting action ensures a consistent seal, reduces the need for retightening, and improves reliability in systems exposed to ongoing thermal cycling.
03 What is the torque spec for constant torque clamps?
The torque specification for constant torque clamps varies by size, structure, and manufacturer guidelines.
These clamps include a spring system that delivers a controlled clamping load once tightened to the proper torque.Applying the recommended torque ensures the spring is activated correctly, allowing it to regulate sealing pressure over time.Under-torquing can result in an insufficient seal, while over-torquing may damage the hose or compromise the clamp’s ability to self-adjust.
For accurate torque values, installers should refer to product datasheets or standards such as SAE J1508.
